一、基础概念
CPU核心数和线程数的关系
核心数:线程数=1:1 ;使用了超线程技术后---> 1:2
CPU时间片轮转机制
又称RR调度,会导致上下文切换
什么是进程和线程
进程:程序运行资源分配的最小单位,进程内部有多个线程,会共享这个进程的资源
线程:CPU调度的最小单位,必须依赖进程而存在。
澄清并行和并发
并行:同一时刻,可以同时处理事情的能力
并发:与单位时间相关,在单位时间内可以处理事情的能力
高并发编程的意义、好处和注意事项
好处:充分利用cpu的资源、加快用户响应的时间,程序模块化,异步化
问题:
线程共享资源,存在冲突;
容易导致死锁;
启用太多的线程,就有搞垮机器的可能
二、认识java里的线程
创建线程的三种方式:
-
继承Thread类
-
实现runable接口
-
实现callable接口,允许有返回值
package com.enjoy.demo.p1.ch1.class1;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
/**
* @Author: BillYu
* @Description:三种方式创建线程
* @Date: Created in 14:56 2019-02-19.
*/
public class NewThread {
/**
* 拓展自Thread类
*/
private static class UseThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("I am extends Thread");
}
}
/**
* 实现Runable接口
*/
private static class UseRun implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("I am implements Runable");
}
}
/**
* 实现Callable接口,允许有返回值
*/
private static class UseCall implements Callable<String>{
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("I am implements Callable");
return "CallResult";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
UseThread useThread = new UseThread();
useThread.start();
UseRun useRun = new UseRun();
new Thread(useRun).start();
Thread t = new Thread(useRun);
// 方法启用且不释放资源
// t.stop();
//java线程是协作式
//interrupt()中断一个线程,并不是强行关闭这个线程,打个招呼,中断标志位置为true
//isInterrupted()判定当前线程是否处于中断状态
//interrupted判定但钱是否处于中断状态,中断标志位置为false
t.interrupt();
UseCall useCall = new UseCall();
FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(useCall);
new Thread(futureTask).start();
System.out.println(futureTask.get());
}
}
安全终止线程
怎么样才能让Java里的线程安全停止工作呢
线程自然终止:自然执行完或抛出未处理异常
stop(),resume(),suspend()已不建议使用,stop()会导致线程不会正确释放资源,suspend()容易导致死锁。
java线程是协作式,而非抢占式
调用一个线程的interrupt() 方法中断一个线程,并不是强行关闭这个线程,只是跟这个线程打个招呼,将线程的中断标志位置为true,线程是否中断,由线程本身决定。
isInterrupted() 判定当前线程是否处于中断状态。
package com.enjoy.demo.p1.ch1.class1;
/**
* @Author: BillYu
* @Description:如何安全中断线程
* @Date: Created in 15:47 2019-02-19.
*/
public class EndThread {
private static class UseThread extends Thread{
public UseThread(String name){
super(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
while (!isInterrupted()){
System.out.println(threadName+" is run");
}
System.out.println(threadName+" interrput flag is "+isInterrupted());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
Thread endThread = new UseThread("endThread");
endThread.start();
Thread.sleep(20);
endThread.interrupt();
}
}
static方法interrupted() 判定当前线程是否处于中断状态,同时中断标志位改为false。
方法里如果抛出InterruptedException,线程的中断标志位会被复位成false,如果确实是需要中断线程,要求我们自己在catch语句块里再次调用interrupt()。
package com.enjoy.demo.p1.ch1.class1;
/**
* @Author: BillYu
* @Description: 更改打断标记
* @Date: Created in 16:56 2019-02-19.
*/
public class HasInterruptedException {
private static class UseThread extends Thread{
public UseThread(String name){
super(name);
}
@Override
public void run(){
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
while (!isInterrupted()){
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
System.out.println(threadName+" interput flag is "+isInterrupted());
//**
interrupt();
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(threadName);
}
System.out.println(threadName+" interput flag is "+isInterrupted());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread endThread = new UseThread("HashInterrputEx");
endThread.start();
Thread.sleep(500);
endThread.interrupt();
}
}
三、更多了解
线程常用方法和线程的状态
线程只有5种状态。整个生命周期就是这几种状态的切换。创建、就绪、运行、阻塞、消亡
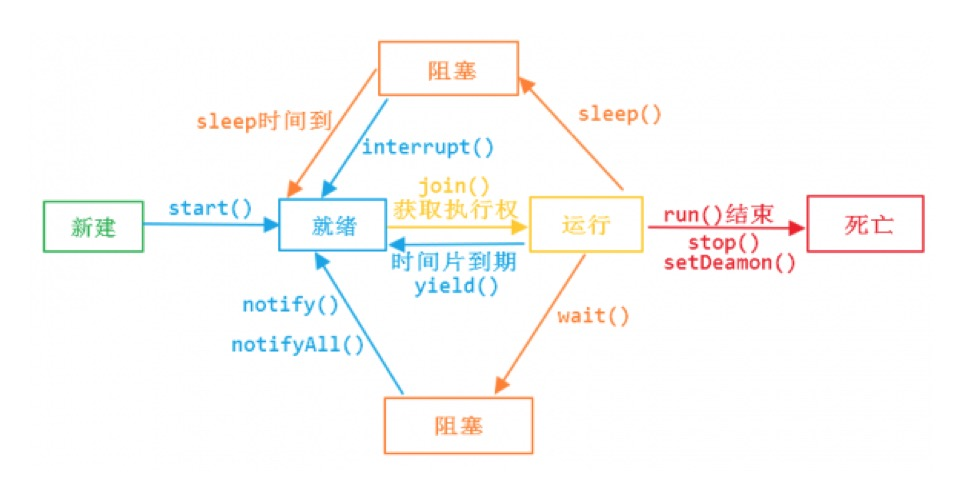
run()和start() :run方法就是普通对象的普通方法,只有调用了start()后,Java才会将线程对象和操作系统中实际的线程进行映射,再来执行run方法。
yield() :让出cpu的执行权,将线程从运行转到可运行状态,但是下个时间片,该线程依然有可能被再次选中运行。
线程的优先级
取值为1~10,缺省为5,但线程的优先级不可靠,不建议作为线程开发时候的手段
守护线程
和主线程共死,finally不能保证一定执行
package com.enjoy.demo.p1.ch1.class1;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
/**
* @Author: BillYu
* @Description:守护线程
* @Date: Created in 14:44 2019-02-20.
*/
public class DaemonThread {
private static class UseThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
//alt+shift+z
try {
while (!isInterrupted()){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+" I am extends Thread.");
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+" interrupt flag is "+ isInterrupted());
} finally {
System.out.println("=======> finally");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
UseThread useThread = new UseThread();
//设置为守护线程 ,和主线程共死,和finally不能保证一定执行
useThread.setDaemon(true);
useThread.start();
Thread.sleep(5);
// useThread.interrupt();
}
}
}
